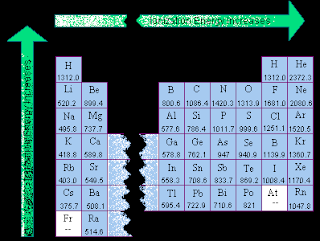
Ionization energy and electronegativity are related to the periodic table. The ionization energy can be thought of as a kind of counter property to electronegativity. Electronegativity is an atoms affinity to draw electrons toward it. The element F is the most electronegative atom. There are some general trend relationships between ionization energy and electronegativity. The ionization energy is the energy it takes to fully remove an electron from the ... Electronegativity is based on an atom's ionization energy and electron affinity. IONIZATION ENERGY, ELECTRONEGATIVITY, RELATIVE SIZES. Ionization Energy. ionization. The amount of energy required to pull an electron off. Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from an element, whereas electron affinity is the amount of attraction a substance has. Ionization Potential or Ionization energy: The amount of energy required to remove an electron. Ionization Energy. The amount of energy required to remove 1 mol of electrons from 1 mol of gaseous atoms to form 1 mol of unipositive gaseous ions. Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity. The process of gaining or losing an electron requires energy. There are two common ways to measure this energy. Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity. IONIZATION ENERGY: A certain amount of energy needed to knock off the electron. Ionization energy is how much energy is needed to remove an electron from the valence shell . The atomic radius increases, as does the energy of the valence electrons. This means it takes less energy to remove an electron, which is what ionization energy.