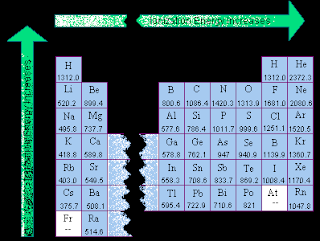
Ionization energy and electronegativity are related to the periodic table. The ionization energy can be thought of as a kind of counter property to electronegativity. Electronegativity is an atoms affinity to draw electrons toward it. The element F is the most electronegative atom. There are some general trend relationships between ionization energy and electronegativity. The ionization energy is the energy it takes to fully remove an electron from the ... Electronegativity is based on an atom's ionization energy and electron affinity. IONIZATION ENERGY, ELECTRONEGATIVITY, RELATIVE SIZES. Ionization Energy. ionization. The amount of energy required to pull an electron off. Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from an element, whereas electron affinity is the amount of attraction a substance has. Ionization Potential or Ionization energy: The amount of energy required to remove an electron. Ionization Energy. The amount of energy required to remove 1 mol of electrons from 1 mol of gaseous atoms to form 1 mol of unipositive gaseous ions. Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity. The process of gaining or losing an electron requires energy. There are two common ways to measure this energy. Ionization Energy and Electron Affinity. IONIZATION ENERGY: A certain amount of energy needed to knock off the electron. Ionization energy is how much energy is needed to remove an electron from the valence shell . The atomic radius increases, as does the energy of the valence electrons. This means it takes less energy to remove an electron, which is what ionization energy.
periodic table contains the element number, element symbol and electronegativity. Learn about the periodic properties or trends in the periodic table of the elements Electronegativity. This page explains what electronegativity is, and how and why it varies around the Periodic Table. Electronegativity values for each element can be found on certain periodic tables.
Showing posts with label electronegativity. Show all posts
Showing posts with label electronegativity. Show all posts
Thursday, October 18, 2012
Saturday, September 29, 2012
PAULING ELECTRONEGATIVITY VALUES
An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number. Linus Pauling's electronegativity scale is the most common. First proposed by Linus Pauling in 1932. According to the great Linus Pauling, electronegativity is “the power of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. Linus Pauling's Development of an Electronegativity Scale. The modern definition of electronegativity is due to Linus Pauling. The first scale of electronegativity was developed by Linus Pauling and on his scale boron has a value of 2.04 on a scale running from from about 0.7. Electronegativity is measured on a variety of scales, the most common being the Pauling scale. Perhaps the most popular method of determining electronegativity is through Linus Pauling (1901-1995)'s model. The concept of electronegativity was put on a quantitative footing in 1932 by Linus Pauling in The Nature of the Chemical Bond. The higher the associated electronegativity number, the more an element or compound attracts electrons towards it. Linus Carl Pauling is the only person to have received two unshared Nobel Prizes - first in 1954 in chemistry. Besides being the greatest architect of chemistry, Pauling was a founder of molecular biology and a pioneer in quantum mechanics. Pauling combined chemistry and physics to solve various puzzles related to the nature of chemical bond. As one of his biographers has written Pauling's understanding of the chemical bond and molecular architecture is probably unsurpassed in the history of chemistry.
Location:
California, USA
Saturday, September 22, 2012
HIGHEST ELECTRONEGATIVITY
The elements with the highest electronegativity are found in the upper right corner of the periodic table, excluding the noble gases.Electronegativity increases as you go from left to right across a period. Elements on the left of the period table have 1 -2 valence electrons. Electronegativity values generally increase from left to right within the Periodic Table of the elements. the relatively low-level quantities of bond lengths, electronegativities, and position in the periodic table. oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine. In the periodic table as we go to the right the size decreases so the electronegativity increases. Fluorine is the most electronegative element and caesium is the least electronegative atom. within metals electronegativity is high for metals at the top of the periodic table since they are small/dense and therfore have small radius. Electronegativity is how badly a element wants to a electron, F is the most electronegative element on the periodic table. periodic table, an atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic weight and the distance that its valence. Electronegativity generally increases as you move from left to right. This is because ionization energy steadily increases.
Thursday, September 20, 2012
Periodic Table Trends
Summary of Periodic Table Trends. Moving Left Right Atomic Radius Decreases Ionization Energy Increases Electronegativity Increases. Periodic table of electronegativity using the Pauling scale → Atomic radius ... molecule to attract electrons to itself. Electronegativity, metallic nature and atomic radius. ... Groups of the Periodic Table; Valence Electrons; Periodic Table Trends: Ionization Energy. Patterns of electronegativity in the Periodic Table. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's "pull" on electrons. It is affected by the distance from the nucleus, electron-electron charge repulsion. Trends in Electronegativity in Periods of the Periodic Table In general, electronegativities of the elements in the same Period increases as you go from left to right. Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.The Pauling scale is the most commonly used. Fluorine (the most electronegative element) is assigned a value of 4.0, and values range down to caesium and francium which are the least electronegative at 0.7. If the atoms are equally electronegative, both have the same tendency to attract the bonding pair of electrons, and so it will be found on average half way between the two atoms. No electronegativity difference between two atoms leads to a pure non-polar covalent bond.A small electronegativity difference leads to a polar covalent bond.A large electronegativity difference leads to an ionic bond.
Wednesday, September 19, 2012
Electronegativity Trends
Periodic table of electronegativity using the Pauling scale. The tendency of an atom in a molecule to attract the shared pair of electron towards itself is called its electronegativity. What really powers a battery is the difference in electronegativity between the materials. Electronegativity values for each element can be found on certain periodic tables. the trends in electronegativity in the periodic table. Trends in Electronegativity in Periods of the Periodic Table. The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract shared electrons is called electronegativity. The higher the electronegativity of an atom, the greater its ability to attract shared electrons. The electronegativity of atoms decreases as you move from top to bottom down a group in the periodic table. GROUP TRENDS: Within a group of the periodic table, electronegativity decreases from top to bottom. Electronegativity is a measure of the attraction an atom involved in a bond .
Location:
California, USA
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)